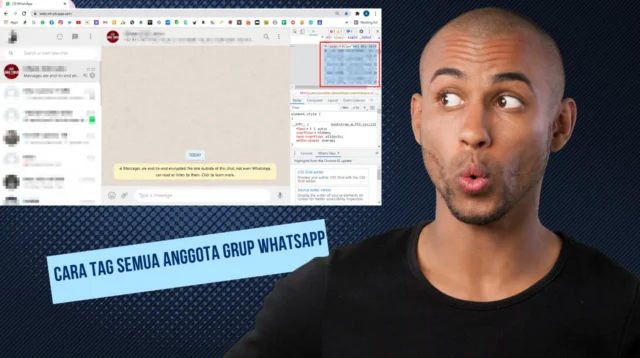
Jika anda pengguna baru dalam mengoperasikan whatsapp, ada tips baru untuk cara tag semua anggota […]
Jika anda pengguna baru dalam mengoperasikan whatsapp, ada tips baru untuk cara tag semua anggota grup whatshapp paling […]
Related News
Headlines
Blog Informasi Berita, Viral, Digital Teknologi Terupdate
14 Januari Diperingati Hari Apa? Simak Jawabannya di Sini.
Tanggal 14 Januari diperingati hari apa? Rupanya tidak banyak peringatan besar yang terjadi pada tanggal […]
Contoh Pesan Pembuka Line Olshop yang Memikat Pelanggan
Sedang mencari contoh pesan pembuka line olshop? Untungnya Anda tidak sendirian karena banyak pemilik toko […]
Manfaat Air Kelapa Hijau Cocok Untuk Kesehatan, Klik Now
Manfaat air kelapa hijau sangat luas tidak hanya sebatas pelepas dahaga yang menyegarkan, tetapi juga […]